
EARTHcare
EarthCARE
Mission Summary
The Earth Clouds, Aerosols, and Radiation Explorer (EarthCARE) satellite mission represents a collaborative effort between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Its objectives are to estimate global profiles of aerosols, clouds, and precipitation properties, and to relate these quantities to the amount of solar and thermal energy escaping the Earth’s atmosphere into space.
By combining comprehensive observations of weather systems with estimates of outgoing energy, the mission aims to improve weather forecasting. The gathered data will provide valuable insights into how clouds and aerosols impact the energy cycle (link to the water/energy cycle page). On the other hand, it will shed light on the influence of increased energy retention in the Earth system, attributed to greenhouse gases, on cloud properties.
Video caption:
EarthCARE will employ high-performance lidar and radar technology that has never been flown in space before, with the objective to deliver unprecedented datasets to allow scientists to study the relationship of clouds, aerosols and radiation at accuracy levels that will significantly improve our understanding of these highly variable parameters.
Instrument payload
The satellite will fly at an altitude of 393 km in a sun-synchronous orbit, ensuring it crosses the Equator at a fixed solar time. The platform will carry four instruments:
- atmospheric lidar
- cloud profiling radar
- multi-spectral imager
- broadband radiometer
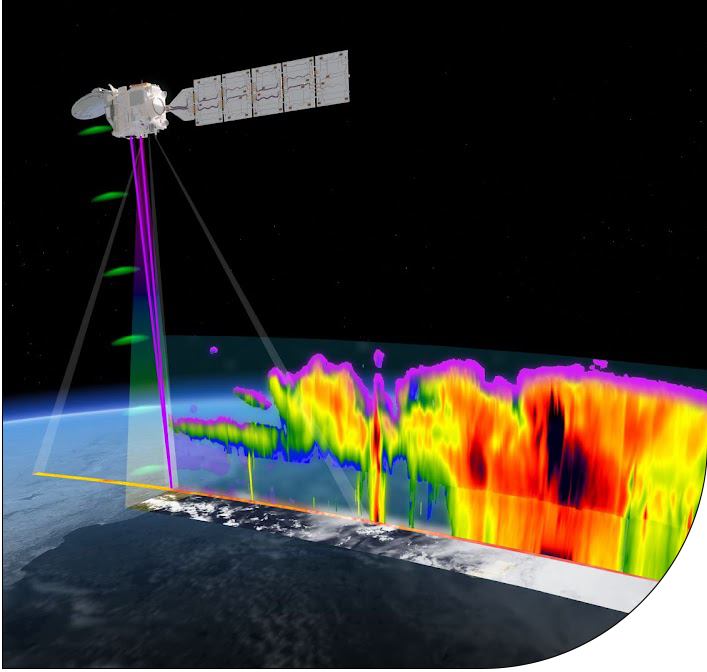
The lidar is designed to measure aerosol and thin cloud profiles, while the radar penetrates deeper into clouds, reaching precipitation near the surface. Its high sensitivity facilitates overlapping with the lidar at cloud tops, ensuring complementary data. Additionally, the radar is first of its kind in space to additionally measure the velocity of detected particles. The imager provides horizontal information on clouds and aerosols, and the combined data from these three instruments enables a three-dimensional scene reconstruction. To verify the consistency of this reconstruction with the energy flow through the atmosphere, a broadband radiometer is employed. The geometry of the satellite measurements is depicted below.
Mission facts
- EarthCARE mission website
- Launched 28th May 2024
- Funding Agency: ESA and JAXA
- Carries four cutting-edge instruments: an atmospheric lidar (ATLID), a cloud profiling radar (CPR), a multi-spectral imager (MSI), and a broad-band radiometer (BBR).
Key Publication
Wehr, T., Kubota, T., Tzeremes, G., Wallace, K., Nakatsuka, H., Ohno, Y., Koopman, R., Rusli, S., Kikuchi, M., Eisinger, M., Tanaka, T., Taga, M., Deghaye, P., Tomita, E., and Bernaerts, D.: The EarthCARE mission – science and system overview, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 16, 3581–3608, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-16-3581-2023, 2023.
EarthCARE UK Science Meeting

On 6th June 25 a meeting was held for the community of UK scientists interested in EarthCARE’s suite of observations across the domains of aerosol, cloud, precipitation, radiation budget, and applications to weather and climate modelling .
Aimed at both current and prospective users, the objective of the meeting was to identify areas of common scientific interest and facilitate coordinated research, particularly seeding consortia for funding applications.

